42nd Amendment, Was it India’s or Indira’s Constitution?
42nd Amendment "is responsive to the aspirations of the people, and reflects the realities of the present time and the future." With these words...
Who will Judge the Judges?
The judges are the ombudsman of the people, there should be a check on their powers to make sure that they don’t enjoy Carte Blanche's powers.
The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019
INTRODUCTION
Laws pertaining to citizenship are governed under Articles 5 to 11 in the Indian Constitution. But it is to be read along with the...
Expanding the Contours of Judicial Independence: A Quasi-Judicial Perspective
INTRODUCTION
The Supreme Court in Rojer Mathew v South Indian Bank Ltd and Ors landed a big blow to the Central Government when it struck...
All you need to know about The Constitution (Fifth Amendment) Act, 1955
Read everything about the Constitution (Fifth Amendment) Act 1955. The need, purpose, terms and the issues dealt by the Constitution is all here.
The Doctrine of Basic Structure in the Indian Constitution: A Critique
The "Doctrine of Basic Structure" is a judge- made doctrine[1] to put a limitation on the amending powers of the Parliament so that the "basic structure of the basic law of the land‟ cannot be amended in exercise of its 'constituent power‘ under the Constitution.
Right to Access Internet Services: The Present Scenario
As the right to access internet is considered by a competent court to be a fundamental right under Article 21, internet services should not be banned unless there exists a genuine threat to security at the gravest degree, such as a war or a cause for a national emergency.
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019: A Toothless Tiger?
Transgender people incorporate Hijras, Eunuchs, Kothis, Aravanis, and others, who have been a part of Indian culture for a considerable length of time. They...
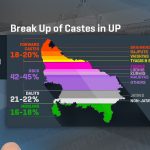
Caste Politics in Contemporary Uttar Pradesh
Will the backward castes always be a tool in the hands of figures of authority to create a new future for themselves?
Why is the abrogation of Article 370 unconstitutional?
A reasonable analysis based on primary legal principles, on the Constitution’s language and on the Court’s own past decisions, will show us that the CAA infracts fundamental rights, in particular the guarantee of equal treatment contained in Article 14.